NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings provides detailed answers for all in-text and exercise Questions. These solutions contain an in-depth explanation of each topic involved in the chapter. Students studying in class 9 can access these solutions for free in PDF format.
All these solutions are prepared by expert teachers and updated for the current academic session. NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (Chemistry) Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings help students to understand the fundamental concepts given in the class 9 Science textbook. We have prepared the answers to all the questions in an easy and well-structured manner. It helps students to grasp the chapter easily.
Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings Intext Questions (Solved)
PAGE NO. 3
Question 1: Which of the following are matter?
Chair, air, love, smell, hate, almonds, thought, cold, cold drink, smell of perfume.
Answer: Anything that occupies space and has mass is called matter. Matter can exist in three physical states – solid, liquid, and gaseous.
Chair and almond are forms of matter in the solid-state.
Cold drink is a liquid state of matter.
Air and smell of perfume are gaseous states of matter.
Note: The sense of smell does not matter. However, the smell or odour of a substance is classified as matter. The smell of any substance (say, perfume) is the gaseous form of that substance which our olfactory system can detect (even at very low concentrations). Hence, the smell of perfume is matter.
Question 2: Give reasons for the following observation:
The smell of hot sizzling food reaches you several metres away, but to get the smell from cold food you have to go close.
Answer: The difference in how we perceive the smell of hot sizzling food versus cold food is due to the way heat affects the movement of molecules:
- Heat Increases Molecule Movement: When food is hot, the heat increases the energy of the aroma molecules, causing them to move faster and spread out more quickly.
- Diffusion: The fast-moving aroma molecules from hot food mix with the air and diffuse (spread out) over a larger area. This means the smell can reach you even from several meters away.
- Cold Slows Down Molecules: For cold food, the aroma molecules move much slower due to the lack of heat. This slower movement means the molecules don’t spread out as far, so you need to be closer to the food to get the smell.
So, heat helps food smell spread further, which is why hot food often smells stronger than cold food.
Question 3: A diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool. Which property of matter does this observation show?
Answer: The observation that a diver is able to cut through water in a swimming pool demonstrates the property of matter known as “fluidity.” Fluidity refers to the ability of a substance to flow and change shape. Water, being a liquid, has this property. It allows the diver to move through it, with the water molecules easily moving around the diver’s body. This ability of liquids and gases to flow and take the shape of their container is what we call fluidity.
Question 4: What are the characteristics of particles of matter?
Answer: The characteristics of particles of matter are:
- Particles of matter have spaces between them.
- Particles of matter are continuously moving.
- Particles of matter attract each other.
PAGE NO. 6
Question 1: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density (density = mass/volume). Arrange the following in order of increasing density − air, exhaust from chimney, honey, water, chalk, cotton, and iron.
Answer: The given substances in the increasing order of their densities can be represented as:
Air < Exhaust from chimney < Cotton < Water < Honey < Chalk < Iron
Question 2: (a) Tabulate the differences in the characteristics of states of matter.
(b) Comment upon the following: rigidity, compressibility, fluidity, filling a gas container, shape, kinetic energy, and density.
Answer: (a) The differences in the characteristics of states of matter are given in the following table.
| Solid state | Liquid state | Gaseous state |
| Definite shape and volume. | No definite shape. Liquids attain the shape of the vessel in which they are kept. | Gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume. |
| Incompressible | Compressible to a small extent. | Highly compressible |
| There is little space between the particles of a solid. | These particles have a greater space between them. | The space between gas particles is the greatest. |
| These particles attract each other very strongly. | The force of attraction between liquid particles is less than solid particles. | The force of attraction is least between gaseous particles. |
| Particles of solids cannot move freely. | These particles move freely. | Gaseous particles are in a continuous, random motion. |
(b) Rigidity: It is the propensity of a substance to continue to remain in its shape when treated with an external force.
Compressibility: It is the attribute of the particles to contract its intermolecular space when exposed to an external force thereby escalating its density.
Fluidity: It is the ability of a substance to flow or move about freely.
Filling the gas container: The particles in a container take their shape as they randomly vibrate in all possible directions.
Shape: It is the definite structure of an object within an external boundary
Kinetic energy: Motion allows particles to possess energy which is referred to as kinetic energy. The increasing order of kinetic energy possessed by various states of matter are:
Solids < Liquids < Gases
Density: It is the mass of a unit volume of a substance. It is expressed as:
d = M/V, where ‘d’ is the density, ‘M’ is the mass and ‘V’ is the volume of the substance
Question 3. Give reasons
(a) A gas fills completely the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) A gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) We can easily move our hand in air but to do the same through a solid block of wood we need a karate expert.
Answer 3: (a) There is little attraction between particles of gas. Thus, gas particles move freely in all directions. Therefore, gas completely fills the vessel in which it is kept.
(b) Particles of gas move randomly in all directions at high speed. As a result, the particles hit each other and also hit the walls of the container with a force. Therefore, gas exerts pressure on the walls of the container.
(c) A wooden table has a definite shape and volume. It is very rigid and cannot be compressed i.e., it has the characteristics of a solid. Hence, a wooden table should be called a solid.
(d) Particles of air have large spaces between them. On the other hand, wood has little space between its particles. Also, it is rigid. For this reason, we can easily move our hands in air, but to do the same through a solid block of wood, we need a karate expert.
Question 4: Liquids generally have lower density as compared to solids. But you must have observed that ice floats on water. Find out why.
Answer: The mass per unit volume of a substance is called density.
(density = mass/volume).
As the volume of a substance increases, its density decreases.
Though ice is a solid, it has large number of empty spaces between its particles. These spaces are larger as compared to the spaces present between the particles of water. Thus, the volume of ice is greater than that of water. Hence, the density of ice is less than that of water. A substance with lower density than water can float on water. Therefore, ice floats on water.
PAGE NO. 9
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale.
(a) 300 K (b) 573 K
Answer:
(a) 300 K = 300 – 273 = 27°C
(b) 573 K = 573 – 273 = 300°C
Question 2: What is the physical state of water at
(a) 250°C (b) 100°C
Answer: (a) Water at 250°C in gaseous state.
(b) At 100°C, water can exist in both liquid and gaseous form. At this temperature, after getting the heat equal to the latent heat of vaporization, water starts changing from liquid state to gaseous state.
Question 3: For any substance, why does the temperature remain constant during the change of state?
Answer: The temperature of a substance remains constant during the change of state because the energy supplied to the substance is used for changing its state, rather than increasing its temperature. For example, when ice melts to become water, the heat energy goes into breaking the bonds between the ice molecules, turning solid ice into liquid water. This process, called the change of state, uses up energy but doesn’t increase the temperature.
Question 4: Suggest a method to liquefy atmospheric gases.
Answer: By applying pressure and reducing the temperature, atmospheric gases can be liquified.
PAGE NO. 10
Question 1: Why does a desert cooler cool better on a hot dry day?
Answer: When a liquid evaporates, the particles of the liquid absorb energy from the surroundings to compensate for the loss of energy during evaporation. This makes the surroundings cool.
A desert cooler cools better on a hot dry day because it works on the principle of evaporative cooling. Here’s how it happens:
When water in the desert cooler evaporates, it takes heat from the surrounding air. This process cools the air. In a dry environment, the air has less moisture, so it can take on more water vapour. This means more water can evaporate from the cooler. On a hot dry day, evaporation happens faster, leading to more cooling.
So, the lower the humidity, the more effectively a desert cooler can work, making it more efficient on hot and dry days.
Question 2: How does water kept in an earthen pot (matka) become cool during summers?
Answer: When a liquid evaporates, the particles of the liquid absorb energy from the container to compensate the loss of energy during evaporation. This makes the remaining water cool.
The earthen pot has tiny holes, and some water seeps out through these holes. When this water on the outside of the pot evaporates, it takes some heat away from the water inside the pot. This makes the water inside cooler, which is why water in a matka feels cool during hot summers.
Question 3: Why does our palm feel cold when we put some acetone or petrol or perfume on it?
Answer: When we put acetone, petrol, or perfume on our palms, it feels cold because these liquids evaporate quickly. Evaporation is a process where a liquid turns into a gas, and it needs heat to happen. As these liquids evaporate, they absorb heat from our palms, making the palms cool.
Question 4: Why are we able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup?
Answer: A liquid has a larger surface area in a saucer than in a cup. Thus, it evaporates faster and cools faster in a saucer than in a cup. For this reason, we are able to sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup.
OR
We can sip hot tea or milk faster from a saucer than a cup because of the larger surface area of the liquid in the saucer. This larger surface area allows the hot liquid to cool down more quickly. When you pour the liquid into a saucer, it spreads out, exposing more of it to the cooler air. This speeds up the cooling process, making it easier and quicker to sip without burning your mouth. In a cup, the liquid’s surface area is smaller, so it takes longer to cool down to a comfortable sipping temperature.
Question 5: What type of clothes should we wear in summers?
Answer: During summers, we sweat more. In summer, it’s best to wear light-colored, loose-fitting cotton clothes. Light colors keep us cool by reflecting sunlight, and cotton being a good absorber of water helps to absorb sweat and allow air to circulate, keeping our body cooler.
OR
In summers, it’s best to wear light-colored, loose-fitting clothes made of natural fabrics like cotton. Light colors reflect more sunlight and absorb less heat, keeping you cooler. Loose clothes allow better air circulation, which helps in evaporating sweat and cooling your body. Cotton fabric is good for summer as it’s breathable and absorbs sweat from your body, aiding in the cooling effect. These choices help to stay comfortable in the heat of summer.
CBSE Class 9 Science Matter in Our Surroundings Exercise Questions and Answers
Question 1: Convert the following temperatures into the Celsius scale.
(a) 293 K (b) 470 K
Answer 1: (a) 293 K = 293 – 273 = 20°C
(b) 470 K = 470 – 273 = 197°C
Question 2 : Convert the following temperatures into the Kelvin scale.
(a) 25°C (b) 373°C
Answer:
(a) 25°C = 25 + 273 = 298 K
(b) 373°C = 373 + 273 = 646 K
Question 3: Give reasons for the following observations.
(a) Naphthalene balls disappear with time without leaving any solid.
(b) We can get the smell of perfume sitting several meters away.
Answer: (a) Naphthalene shows the property of sublimation. Evaporation of naphthalene takes place easily and so it disappears during course of time without leaving a solid.
(b) Perfumes vaporize very fast and its vapours diffuse into air easily. That is why we can smell perfume sitting several meters away.
Question 4: Arrange the following in increasing order of forces of attraction between the particles – water, sugar, oxygen.
Answer: Oxygen < Water < Sugar.
Question 5: What is the physical state of water at —
(a) 25°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 100°C?
Answer: (a) Liquid
(b) Solid and Liquid
(c) Liquid and Vapours
Question 6: Give two reasons to justify:
(a) Water at room temperature is a liquid.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature.
Answer: (a) Water at room temperature is a liquid because it has fluidity and has a definite volume but no definite shape.
(b) An iron almirah is a solid at room temperature because it is rigid and has a definite shape.
Question 7: Why is ice at 273 K more effective in cooling than water at the same temperature?
Answer: Ice at 273 K is less energetic than water. It is because of the difference in the latent heat of fusion which is present in water at the same temperature in the form of extra energy.
Question 8: What produces more severe burns, boiling water or steam?
Answer: Steam produces more severe burns than boiling water. This is because steam has more energy than boiling water, present in it in the form of latent heat of vaporization.
Question 9: Name A, B, C, D, E and F in the following diagram showing change in its state:
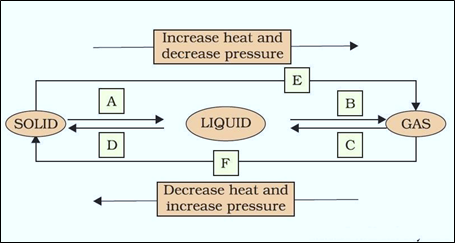
Answer:
A: Melting (or) fusion (or) liquefaction
B: Evaporation (or) vaporization
C: Condensation
D: Solidification
E: Sublimation
F: Sublimation