NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Crop Production and Management helps students to clear all their doubts. These solutions provide you with the answers to all the questions given in the NCERT textbook. CBSE Class 8 Science Chapter 1 Solutions is prepared by expert teachers as per the latest CBSE syllabus and guidelines.
Solving NCERT Solutions will help you to understand the concepts related to Crop Production and Management. NCERT Solutions for Class 8 Science Chapter 1 contains an in-depth explanation of each question of NCERT Science textbook. These solutions cover important concepts in different patterns like MCQs and short answer questions, worksheets and more and help you top score good marks in the exam.
Class 8 Science Crop Production and Management Questions and Answers
Exercise Questions
Question 1: Select the correct word from the following list and fill in the blanks.
float, water, crop, nutrients, preparation
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called _____________.
(b) The first step before growing crops is _____________ of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would _____________ on top of water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and _____________ and _____________ from the soil are essential.
Answer:
(a) The same kind of plants grown and cultivated on a large scale at a place is called the crop.
(b) The first step before growing crops is the preparation of the soil.
(c) Damaged seeds would float on top of the water.
(d) For growing a crop, sufficient sunlight and water and nutrients from the soil are essential.
Question 2. Match items in column A with those in column B.
| A | B |
| (i) Kharif crops | (a) Food for cattle |
| (ii) Rabi crops | (b) Urea and superphosphate |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes |
| (iv) Organic manure | (d) Wheat, gram, pea |
| (e) Paddy and maize |
Answer:
| (i) Kharif crops. | (e) Paddy and maize. |
| (ii) Rabi crops. | (d) Wheat, gram, pea. |
| (iii) Chemical fertilisers. | (b) Urea and superphosphate. |
| (iv) Organic manure. | (c) Animal excreta, cow dung urine and plant wastes. |
Question 3. Give two examples of each.
(a) Kharif crop
(b) Rabi crop
Answer: Kharif crop: Paddy, maize, soyabean, groundnut, cotton, etc.
Rabi crop: Wheat, gram, pea, mustard, etc.
Question 4: Write a paragraph in your own words on each of the following.
(a) Preparation of soil
(b) Sowing
(c) Weeding
(d) Threshing
Answer:
(a) Preparation of Soil: This is the first step in farming. It involves loosening the soil to help plant roots grow better. This also helps in removing weeds and old plant parts, making the soil better for new crops.
(b) Sowing: Sowing is when farmers plant seeds in the ground. Sowing is the most important part of crop production. Before sowing, good-quality seeds are selected. Seeds can be sown by seed drill or manually.
(c) Weeding: Weeding means taking out unwanted plants from the field. These unwanted plants, called weeds, take nutrients and space from the crops. Removing them helps the crops grow better. Weeds can be removed either manually by using tools like khurpi or by using weedicides like 2, 4 – D.
(d) Threshing: After crops are harvested, threshing separates the grains from the rest of the plant. This can be done by hand or with machines. It’s an important step to get the grains ready for use or storage.
Question 5: Explain how fertilisers are different from manure.
Answer5: The main Differences between Fertiliser and Manure are as follows:
| Fertilisers | Manures |
| A fertiliser is an inorganic salt. | Manure is a natural substance obtained by the decomposition of cattle dung, human waste and plant residues. |
| A fertiliser is prepared in factories. | Manure can be prepared in the fields. |
| A fertiliser does not provide any humus to the soil. | Manure provides a lot of humus to the soil. |
| Fertilisers are very rich in plant nutrients like nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. | Manure is relatively less rich in plant nutrients. |
Question 6: What is irrigation? Describe two methods of irrigation which conserve water.
Answer: The supply of water to crops at different intervals is called irrigation. The two methods of irrigation which conserve water are as follows:
Sprinkler System: Under this method, the perpendicular pipes, having rotating nozzles on top, are joined to the main pipeline at regular intervals. When water is allowed to flow through the main pipe under pressure with the help of a pump, it escapes from the rotating nozzles. It gets sprinkled on the crop as if it is raining.
Drip system: In this system, the water falls drop by drop just at the position of the roots. It is the best technique for watering fruit plants, gardens and trees. Water is not wasted at all. It is a boon in regions where availability of water is poor.
Question 7: If wheat is sown in the kharif season, what would happen? Discuss.
Answer: Wheat is a rabi crop, hence it requires cold climatic conditions to be grown properly. If it is sown in the kharif season, it will not grow or may get destroyed due to excessive rains in the kharif season.
Question 8: Explain how soil gets affected by the continuous plantation of crops in a field.
Answer: Soil supplies mineral nutrients to the crop. These nutrients are essential for the growth of plants. Continuous growing of crops in the same field makes the soil poorer in certain nutrients. This makes the soil infertile. And then, to replenish the soil with nutrients farmers need to add manures to the soil.
OR
When crops are planted continuously in the same field, the soil can get affected in a few ways:
- Nutrient Depletion: Each crop takes specific nutrients from the soil. Continuous planting of the same crop can deplete the soil of these nutrients, making it less fertile.
- Soil Erosion: Without giving the soil time to recover, it can become weak and more prone to erosion, especially by wind and water.
- Build-up of Pests and Diseases: Continuous cropping can lead to a build-up of pests and diseases specific to that crop, which can be harmful to the soil and future crops.
- Soil Structure Deterioration: Continuous plantation can also lead to the deterioration of soil structure, making it harder for plant roots to grow.
To prevent these issues, practices like crop rotation and resting the soil are important.
Question 9: What are weeds? How can we control them?
Answer: Weeds ae unwanted plants that grow among crops. They compete with crops for nutrients, light, and space. Weeds can be removed by uprooting or cutting them close to the ground, from time to time. This is done with the help of a khurpi. Weeds are also controlled by using certain chemicals, called weedicides, like 2, 4–D. These are sprayed in the fields to kill the weeds.
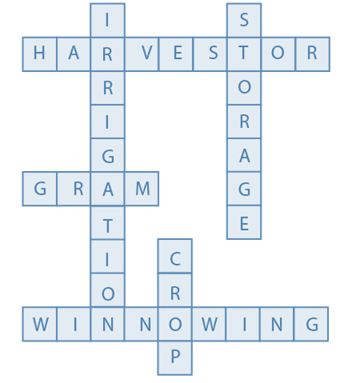
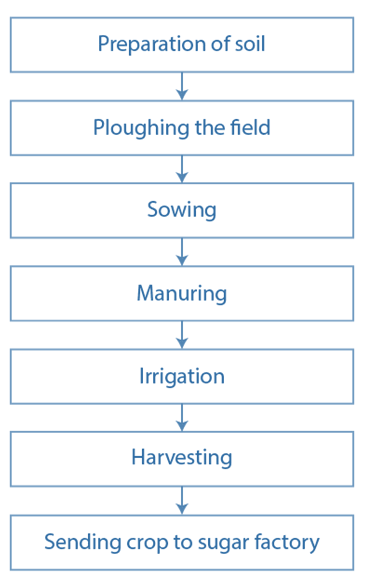
Question 10: Arrange the following boxes in proper order to make a flow chart of sugarcane crop production.
Answer:
Question 11: Complete the following word puzzle with the help of clues given below.
Down
1. Providing water to the crops.
2. Keeping crop grains for a long time under proper conditions.
5. Certain plants of the same kind grown on a large scale.
Across
3. A machine used for cutting the matured crop.
4. A rabi crop that is also one of the pulses.
6. A process of separating the grain from chaff.
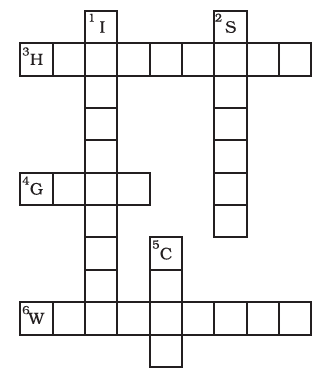
Answer:
Down
1. Irrigation
2. Storage
5. Crop
Across
3. Harvester
4. Gram
6. Winnowing