NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Social Science Economics Chapter 2 People as Resource contains the solutions to the exercises given in the textbook. These solutions also contain answers to all the let’s discuss questions. These NCERT solutions are useful for students as they help to score high marks in the exams.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Let’s Discuss
Let’s Discuss Page no. 17
Question 1: Looking at the photograph can you explain how a doctor, teacher, engineer and a tailor are an asset to the economy?
Answer: (i) A population becomes human capital when there is an investment made in the form of education training and medical care.
(ii) Human capital is the stack of skills and productive knowledge embodied in them.
(iii) Investment made in the form of education and training in making a doctor, a teacher an engineer and a tailor, have increased their capabilities of providing different services to the people of the country and therefore they are an asset to the economy of a nation
Let’s Discuss Page no. 18
Question 1: Do you notice any difference between the two friends? What are those?

Answer: The differences between the two friends Sakal and Vilas were
(i) Vilas father died when Vilas was two years old whereas Sakal was living with his parents.
(ii) Sakal went to school but Vilas did not go to school.
(iii) Sakal was interested in studies whereas Vilas was not interested in studies.
(iv) Sakal did a course in computers and became employed whereas Vilas remained illiterate and was not employed
(v) The condition of Sakal and his family became better whereas Vilas and his family lived in poverty.
Let’s Discuss Page no. 21
Study the graph and answer the following questions:
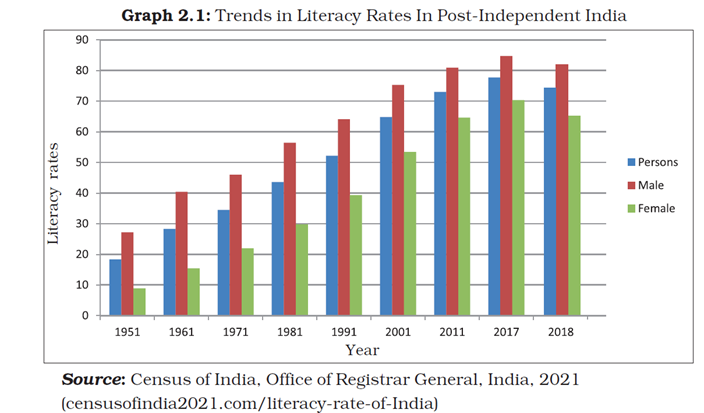
Question 1: Has the literacy rates of the population increased since 1951?
Answer: Yes, the literacy rates of the population have increased since 1951 as shown below.
Question 2: In which year India has the highest literacy rates?
Answer: India has the highest literacy rates in 2017.
Question 3: Why literacy rate is high among the males of India?
Answer: India traditionally has a patriarchal male-dominated society where more importance is given to males. Culturally due to division of labour, the males go out of their homes and get better access to education. Girls often had to stay home and help instead of going to school. Poor families due to monetary constraints prefer to send only their sons to school and not their daughters.
Question 4: Why are women less educated than men?
Answer: Women are less educated than men primarily due to historical and cultural norms that prioritize men’s education and economic roles. Traditionally, girls are assigned to do domestic work limiting their access to education. Economic constraints further accelerate this disparity, as families tend to invest more in boys, viewing them as future earners. Hence women are less educated than men.
Question 5: How would you calculate literacy rate in India?
Answer: The literacy rate can be calculated on the basis of the formula i.e., the number of literate people divided by the population multiplied by 100.

Question 6: What is your projection about India’s literacy rate in 2025?
Answer: The projection for India’s literacy rate in the year 2025 would be between 85% to 90%.
Let’s Discuss Page no. 23
Discuss this table in the classroom and answer the following questions.
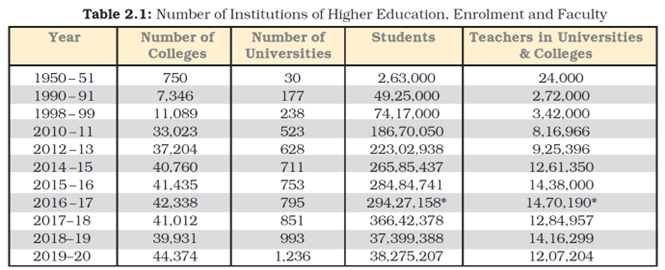
Question 1: Is the increase in the number of colleges adequate to admit the increasing number of students?
Answer: No, the increase in the number of colleges is not adequate to admit the increasing number of students because the number of students is increasing at a faster rate compared to the colleges being established.
Question 2: Do you think we should have more number of universities?
Answer: Seeing the ever-increasing number of students, we should establish more universities to cater to their needs. But at the same time, greater stress should be on opening more and more colleges.
Question 3: What is the increase noticed among the teachers in the year 2015-16.
Answer: There was an increase of 1,76,650 teachers in the year 2015-16 compared to 2014-2015.
Question 4: What is your idea about future colleges and universities?
Answer: In future colleges and universities, stress should be on vocationalisation of education. There should also be a focus on distance education, and convergence of formal and informal, distance and IT education institutions. Colleges should be set up in rural areas to benefit rural students. Colleges and universities should focus on providing student-centred education.
Let’s Discuss Page no. 23-24
Study Table 2.2 and answer the following questions.
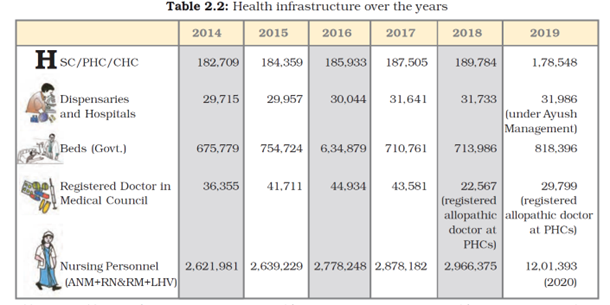
Question 1: What is the percentage increase in dispensaries from 1951 to 2020?
Answer: Missing
Question 2: What is the percentage increase in doctors and nursing personnel from 1951 to 2020?
Answer: Missing
Question 3: Do you think the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is adequate for India? If not, why?
Answer: No, the increase in the number of doctors and nurses is Inadequate because the ratio of both doctors and nursing personnel is still too low for India’s population.
Question 4: What other facilities would you like to provide in a hospital?
Answer: Other facilities we would like to provide in a hospital — (i) Hospitals should be spotlessly clean and hygienic.
Question 5: Discuss about the hospital you have visited?
Answer: I have visited the Anand Hospital in our city
(i) It is a 200 bed multi-specialist hospital and provides high class medical facilities.
(ii) It has state of the art operation theatres
(iii) It has various machines to carry out different kinds of tests like ultrasound, blood bank. MRI, etc.
(iv) It has a well-equipped pathology lab.
(v) It has a number of specialists in different branches of medicine.
(vi) It caters to the needs of the entire city and also to the surrounding rural areas.
(vii) It is centrally air-conditioned. It also has a medical store.
(viii) The only drawback is that being a private hospital the treatment for the patients is costly.
Question 6: Can you draw a graph using this table
Answer: Do it yourself.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Economics Chapter 2 Exercises
Exercises Questions and Answers
Question 1: What do you understand by ‘people as a resource’?
Answer: The concept of “people as a resource” refers to viewing the population in terms of their abilities, talents, and skills that can be utilized for economic development. It emphasizes the idea that humans, through their knowledge, learned abilities, and health, contribute to the creation of wealth. When investments are made in education, training, and healthcare, the population becomes a more valuable asset, termed human capital.
Question 2: How is human resource different from other resources like land and physical capital?
Answer: Human resources make use of other resources like land and physical capital to produce an output. Unlike physical assets, which are static, human resources can grow and improve through education and training, making them a dynamic and crucial asset for economic development.
Question 3: What is the role of education in human capital formation?
Answer: Education plays a crucial role in human capital formation by enhancing individuals’ knowledge, skills, and abilities, making them more productive. It equips people with the competencies needed for employment, fosters innovation, and improves workforce quality. As a result, education is a vital investment in human capital, leading to better job opportunities, higher earnings, and economic growth.
Question 4: What is the role of health in human capital formation?
Answer: The role of health in human capital formation is fundamentally important. Good health increases an individual’s ability to learn, work efficiently, and be more productive. When people are healthy, they can attend school regularly, engage in training, and perform their jobs effectively, contributing positively to economic growth. Healthier populations are more resilient, have longer working lives, and require less spending on healthcare, freeing up resources for other investments.
Question 5: What part does health play in the individual’s working life?
Answer: Health plays a crucial role in an individual’s working life by directly impacting their productivity, efficiency, and ability to work. Good health ensures that individuals can perform their job tasks effectively. Furthermore, a healthy individual is likely to have a longer working life, contributing more significantly to economic productivity over time. Conversely, poor health can lead to reduced work capacity, earlier retirement, and higher healthcare costs, affecting both individual earnings and overall economic performance.
Question 6: What are the various activities undertaken in the primary sector, secondary sector and tertiary sector?
Answer: The various activities undertaken in the primary, secondary, and tertiary sectors are as follows:
- Primary Sector: This sector involves activities related to the extraction and production of natural resources. It includes agriculture, farming, animal husbandry, forestry, fishing, and mining. Activities in this sector are directly connected to the environment and involve the utilization of earth’s natural resources.
- Secondary Sector: The secondary sector deals with the transformation of raw materials into goods. This includes manufacturing, processing, and construction.
- Tertiary Sector: The tertiary sector provides services instead of goods. This sector includes a wide range of activities like retail, transportation, education, healthcare, finance, insurance, entertainment, and hospitality services.
Question 7: What is the difference between economic activities and non-economic activities?
Answer: The activities that add value to the national income are called economic activities. They can be divided into two types: market activities and non-market activities. Market activities involve the activities performed for pay or profit and non-market activities include the production done for self-consumption.
The activities that add no value to the national income are called non- economic activities. These activities might include volunteering for a charity, pursuing hobbies, or household work done without pay.
Question 8: Why are women employed in low paid work?
Answer: Education and skill are the major determinants of the earning of any individual in the market. Many women have limited access to education and professional training, which restricts their opportunities to higher-paying jobs. Women often work in sectors where there is no job security. and legal protections. This absence of basic facilities contributes to their concentration in lower-paid jobs.
Question 9: How will you explain the term unemployment?
Answer: Unemployment refers to the situation when individuals who are willing to work at prevailing wages cannot find jobs. It indicates a condition where people actively seeking employment remain jobless. This state not only reflects wasted manpower resources but also contributes to the economic and psychological burden on society and individuals.
Question 10: What is the difference between disguised unemployment and seasonal unemployment?
Answer: Disguised unemployment: When more persons are working in a job than actually required, the situation is termed as disguised unemployment. For example, if a farm requires five workers but employs eight, the extra three are disguisedly unemployed because removing them wouldn’t affect output.
Seasonal unemployment: Seasonal unemployment occurs when people are able to find jobs only during some months of the year. For Example, Agricultural labourers find work only during the busy seasons, i.e., sowing, harvesting, weeding and threshing. This is because of the seasonal character of agriculture in India.
Question 11: Why is educated unemployed, a peculiar problem of India?
Answer: Educated unemployment in India is peculiar due to the mismatch between the education system and market demands. Despite high levels of education, many graduates struggle to find jobs suited to their qualifications. This situation is exacerbated by a focus on theoretical knowledge over practical skills. Additionally, the growth in higher education has not been matched by an equivalent expansion in job opportunities, leading to an oversupply of qualified candidates for a limited number of positions.
Question 12: In which field do you think India can build the maximum employment opportunity?
Answer: India can build maximum employment opportunities in the Information Technology (IT), services sectors, and business process outsourcing. Additionally, the renewable energy sector, especially solar and wind energy, holds significant potential for job creation. Agriculture, through agro-based industries and modern farming techniques, and the manufacturing sector under initiatives like “Make in India” can also generate substantial employment. Finally, the healthcare and education sectors, due to the country’s large population and growing demand for quality services, present considerable opportunities for employment growth.
Question 13: Can you suggest some measures in the education system to mitigate the problem of the educated unemployed?
Answer: Some measures that can be taken in the education system to mitigate the problem of educated unemployed are as follows:
- Aligning educational curricula with industry demands.
- Integrating vocational training and skill development programs into the curriculum.
- Encourage entrepreneurship through dedicated courses and support systems, enabling students to start their own ventures.
- Incorporating courses on emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, renewable energy, and biotechnology to prepare students for future job markets.
- Regularly updating the curriculum to reflect the latest developments in various fields and include contemporary skills and knowledge.
Question 14: Can you imagine some village which initially had no job opportunities but later came up with many?
Answer: There can be many examples of such villages. When an infrastructure project or some industry develops near a village, employment generation takes place. Gurgaon can be a very good example. Before the beginning of the Maruti Udyog Limited, Gurgaon used to be a small village. Subsequent development of industry changed the situation in Gurgaon.
Question 15: Which capital would you consider the best — land, labour, physical capital and human capital? Why?
Answer: Human capital makes use of the other resources like land, labour and physical capital to produce an output. The other resources cannot become useful on their own. Hence, human capital may well be considered the best among all the resources.